10 RTC
1 RTC 实时时钟概述
RTC(Real Time Clock,实时时钟)是一个专门用来记录时间的硬件设备,是计算机系统中的重要组件。RTC 的主要作用是在系统断电或关机状态下继续保持时间计数,确保系统重新启动后能够获得准确的时间信息。
1.1 HYM8563 RTC 芯片规格
基本参数
- 芯片型号: HYM8563
- 接口类型: I2C 总线接口
- 工作电压: 1.0V ~ 5.5V
- 备用电压: 1.0V ~ 5.5V
- I2C 地址: 0x51 (7位地址)
- I2C 速率: 支持标准模式(100kHz)和快速模式(400kHz)
时钟精度
- 晶振频率: 32.768kHz
- 时钟精度: ±20ppm (25°C)
- 温度范围: -40°C ~ +85°C
- 时钟误差: 约 ±1 分钟/月 (25°C)
1.2 RTC 系统架构
硬件连接
RK3568J SoC
├── I2C2 接口
│ ├── SDA (数据线)
│ ├── SCL (时钟线)
│ └── INT (中断线)
└── HYM8563 RTC芯片
├── 32.768kHz 晶振
├── CR2032 纽扣电池
└── 电源管理电路软件架构
应用层
├── date, hwclock 命令
├── timedatectl 工具
└── 用户应用程序
│
内核层
├── RTC 子系统
├── HYM8563 驱动
├── I2C 子系统
└── 设备树配置
│
硬件层
├── I2C 控制器
└── HYM8563 芯片1.3 为什么需要 RTC
Linux 的系统时间(wall time)只能在系统运行时使用,系统关机时间就丢失了,而 RTC 可以在系统关闭后,依靠外部电池或其他电源继续工作,将时间保存下来。这对于以下场景特别重要:
- 无网络环境: 无法通过 NTP 同步时间的离线设备
- 数据完整性: 需要准确时间戳的数据记录系统
- 定时任务: 需要在特定时间自动启动的系统
- 法规要求: 某些行业对时间精度有严格要求
2 RTC 的使用
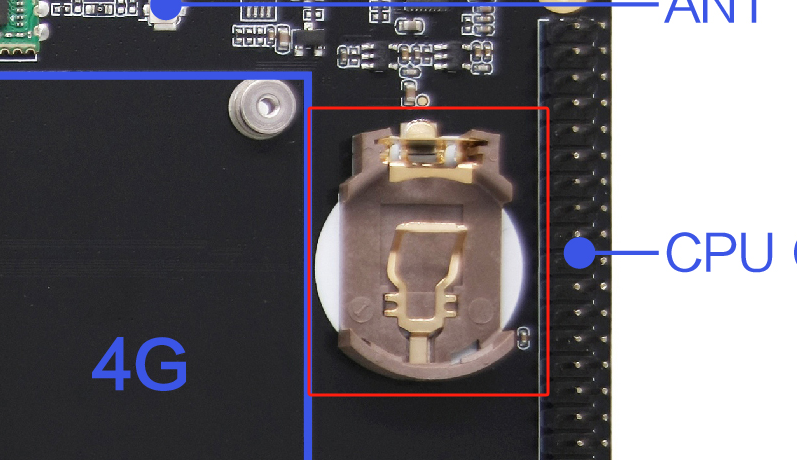
开发板使用外部 RTC(hym8563),默认关闭了 rk809 的 rtc 功能。
使用外部 RTC 时需要接入纽扣电池
1)RTC 用户接口调用
Linux 提供了三种用户空间调用接口。在板卡中对应的路径为:
SYSFS 接口:/sys/class/rtc/rtc0/
PROCFS 接口: /proc/driver/rtc
IOCTL 接口: /dev/rtc0
2)SYSFS 接口
cat proc/driver/rtc
rtc_time : 02:01:53
rtc_date : 2025-02-21
alrm_time : 00:00:00
alrm_date : 1970-01-01
alarm_IRQ : no
alrm_pending : no
update IRQ enabled : no
periodic IRQ enabled : no
periodic IRQ frequency : 1
max user IRQ frequency : 64
24hr : yes3)PROCFS 接口
cat /proc/driver/rtc
rtc_time : 09:50:05
rtc_date : 2024-10-21
alrm_time : 00:00:00
alrm_date : 1970-01-01
alarm_IRQ : no
alrm_pending : no
update IRQ enabled : no
periodic IRQ enabled : no
periodic IRQ frequency : 1
max user IRQ frequency : 64
24hr : yes4)IOCTL 接口
可以参考内核文档作为例子 kernel/tools/testing/selftests/timers/rtcpie.c
3 常用的命令
date // 修改系统时钟,具体命令使用可以 man 下
hwclock -s // 将硬件时间同步到系统时间
hwclock -w // 将系统时间同步到硬件时间
timedatectl // 显示系统时间等
# 以下手动设置时间或者网络同步时间后,-w 将系统时间写入到硬件 rtc,-s 再将 rtc 时间写回系统,这样每次重启板卡都会进行 rtc 时间同步到系统时间。
sudo date -s "2025-02-14 08:00:00" // 手动设置时间
sudo hwclock -w // 系统时间同步到硬件 rtc
sudo hwclock -s // 硬件 rtc 同步到系统3.1 NTP 时间同步
# 安装 NTP 客户端
sudo apt-get install ntp ntpdate
# 手动同步时间
sudo ntpdate -s time.nist.gov
# 配置 NTP 服务器
sudo nano /etc/ntp.conf
# 添加 NTP 服务器
server 0.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 1.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 2.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 3.pool.ntp.org iburst
# 启动 NTP 服务
sudo systemctl enable ntp
sudo systemctl start ntp
# 同步到硬件 RTC
sudo hwclock -w3.2 使用 timedatectl 管理时间
# 查看时间状态
timedatectl status
# 设置时区
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
# 启用 NTP 同步
sudo timedatectl set-ntp true
# 手动设置时间
sudo timedatectl set-time "2025-02-14 08:00:00"
# 同步到硬件 RTC
sudo hwclock -w4 故障排除
4.1 RTC 设备无法识别
检查步骤:
# 检查 I2C 设备
i2cdetect -y 2
# 检查设备树配置
cat /proc/device-tree/i2c@*/rtc@*/compatible
# 检查内核日志
dmesg | grep -i rtc
dmesg | grep -i hym8563
# 检查驱动加载
lsmod | grep rtc解决方案:
# 手动加载 RTC 驱动
sudo modprobe rtc-hym8563
# 检查 I2C 总线配置
sudo i2cget -y 2 0x51 0x004.2 时间不准确或漂移
诊断方法:
# 比较系统时间和 RTC 时间
date
hwclock -r
# 检查时钟源
cat /sys/devices/system/clocksource/clocksource0/current_clocksource
# 监控时钟漂移
ntpq -p解决方案:
# 校准 RTC 时间
sudo ntpdate -s time.nist.gov
sudo hwclock -w
# 调整系统时钟
sudo adjtimex -t4.3 闹钟功能异常
检查要点:
# 检查中断配置
cat /proc/interrupts | grep rtc
# 检查唤醒源
cat /sys/power/wakeup_count
# 测试闹钟功能
echo +10 > /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm
cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm4.4 电池电量不足
检查方法:
# 检查电池电压
cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/voltage
# 检查低电压标志
cat /proc/driver/rtc | grep voltage