Qwen3-langchain-AI Agent
一、Introduction
LangChain is a framework specially designed for developing large-scale language model (LLM) applications. It supports the integration of external tools, data resources and management of interaction logic, and helps build complex AI applications such as intelligent dialogue and document analysis. The main goal of this project is to simplify the interaction with documents and extract valuable information by using natural languages. This project uses LangChain and Qwen3-7b to provide users with a smooth and natural conversation experience.
1、Characteristics
- Complete local reasoning.
- Support multiple document formats PDF, DOCX, TXT.
- Chat with the document content, ask questions and get relevant answers according to the document.
- User friendly interface to ensure smooth interaction.
2、Project directory
Project directory for personal demonstration
|-- ChatDoc-TPU
|-- data
|-- db_tpu -- Knowledge base persistence directory
|-- uploaded -- uploaded file directory
|-- models
|-- bert_model -- BERT model
|-- qwen_model -- qwen-7B model
|-- chat
|-- chatbot.py -- ChatDoc business logic script
|-- charglm3 -- charglm3 code
|-- qwen -- qwen code
|-- embedding -- text embedding model
|-- docs -- environment installation document
|-- static -- Image file in README
|-- README.md -- README
|-- config.ini -- inference model configuration file
|-- requirements.txt -- project dependency
|-- run.sh -- Start script
|-- web_demo_st.py -- Page interaction script二、Operation steps
1、Prepare Python environment, data and model
1.1 First confirm that python>3.8, create and enter the virtual environment
sudo apt update
#Check the python version. If not, upgrade it
python3 --version
# Create virtual environment (excluding pip package)
# !!! Every time you run, you should switch the virtual environment according to the steps!!!
cd /data
# Create virtual environment (excluding pip)
python3.10 -m venv --without-pip myenv
# Enter the virtual environment
source myenv/bin/activate1.2 Copy the official ChatDoc - TPU project directory (or upload the file to/data in the box after copying)
git clone https://github.com/wangyifan2018/ChatDoc-TPU
cd ChatDoc-TPU
# Install the relevant pip package
pip3 install -r requirements.txt -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
#Check the pip package
pip list1.3 Install the oil
This routine ` depends on the new version of sail ', and the old version needs to be updated.Sail_Install_Guide
2 Start
Return to the ChatDoc TPU home directory and start the program
# Start Qwen-7b using the default path, and the model and configuration file will be downloaded automatically
./run.sh --model qwen7b --dev\_id 0Of course, other models can also be selected. The reference template is as follows:
usage: ./run.sh [--model MODEL] [--dev_id DEV_ID] [--server_address SERVER_ADDRESS] [--server_port SERVER_PORT]
--model: select a model, and the optional value is chatglm3/qwen. The default is chatglm3.
--dev_id: The TPU device ID used for inference. The default is 0.
--server_address: web server address. The default is 0.0.0.0.
--server_port:web sever port. If it is not set, it will be automatically allocated from 8501.3、Operating instructions
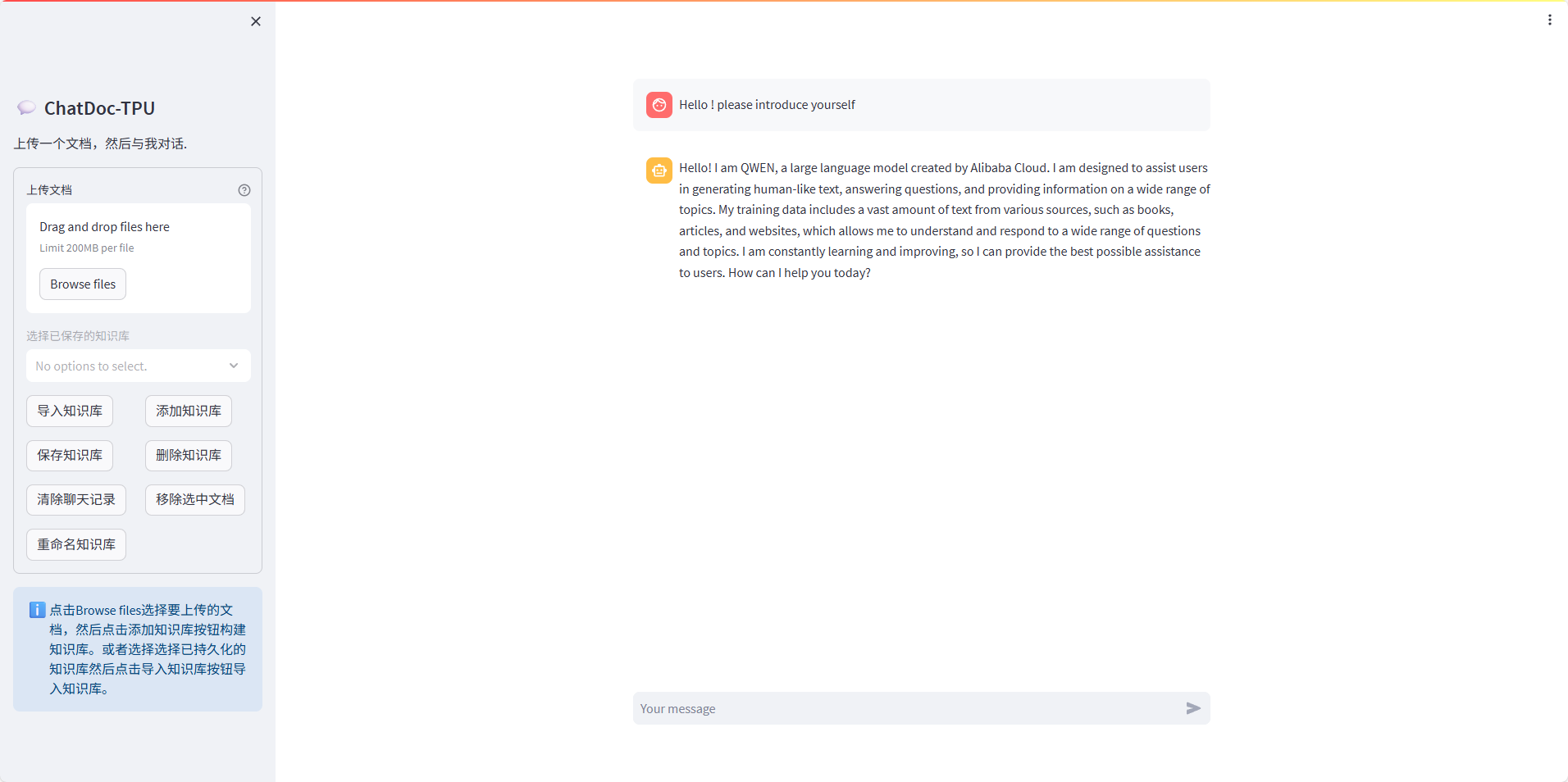
3.1 Interface Introduction
ChatDoc consists of a control area and a chat conversation area. The control area is used to manage documents and knowledge base, and the chat dialog area is used to enter and accept messages.
Area 10 in the above figure is the currently selected document of ChatDoc. If Area 10 is empty, that is, ChatDoc is still talking with ChatDoc in the chat conversation area without any document selected, then ChatDoc is a ChatBot relying solely on LLM.
3.2 Uploading documents
Click '1' to select the document to upload, and then click '4' to build the knowledge base. Then the embedding document will be selected and displayed in the No. 10 area, and then the dialogue can be started. We can upload documents repeatedly. Documents successfully embedded will enter the No. 10 area.
3.3 Persistent Knowledge Base
The selected document in area 10 will be cleared when the user refreshes or closes the page. If users need to save these embedded documents, they can choose to persist the knowledge base. The knowledge base can be loaded without embedding calculation when entering next time. The specific method is to click the button '5' when Area 10 is not empty. The name of the knowledge base is all document names connected by commas.
3.4 Import Knowledge Base
Users can view the current persistent knowledge base from the selection box '2'. After selecting the knowledge base we need to load, click the button '3' to import the knowledge base. When you are finished, you can start the conversation. Note that the knowledge base of the cpu version and the knowledge base of the tpu version cannot be mixed. If the tpu version program is started, the persistent knowledge base of the cpu version cannot be loaded; If you start the cpu version program, you cannot load the persistent tpu version knowledge base.
3.5 Deleting Knowledge Base
When the user needs to delete the local persistent knowledge base, he can select the knowledge base to delete from the selection box '2', and then click the button '6' to delete the knowledge base.
3.6 Rename the knowledge base
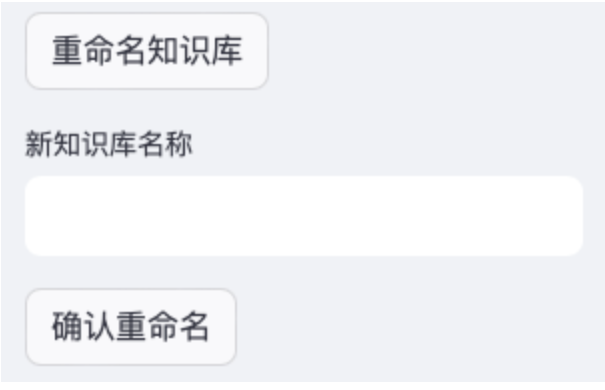
Because the name of the knowledge base is a combination of the names of its documents, it inevitably causes the problem that the name of the knowledge base is too long. ChatDoc provides a function to modify the name of the knowledge base. Select the knowledge base we want to modify in the selection box '2', and then click the button '9' to rename the knowledge base. Then ChatDoc will pop up an input box and a confirmation button, as shown in the above figure. Enter the modified name in the output box, and then click the Confirm Rename button.
3.7 Clear chat record
Click the button '7' to clear the chat record in the chat dialog area. Others will not be affected.
3.8 Remove Selected Documents
Click the button '8' to clear Area 10 and clear the chat record.
