Serial port communication
1. Serial port pins
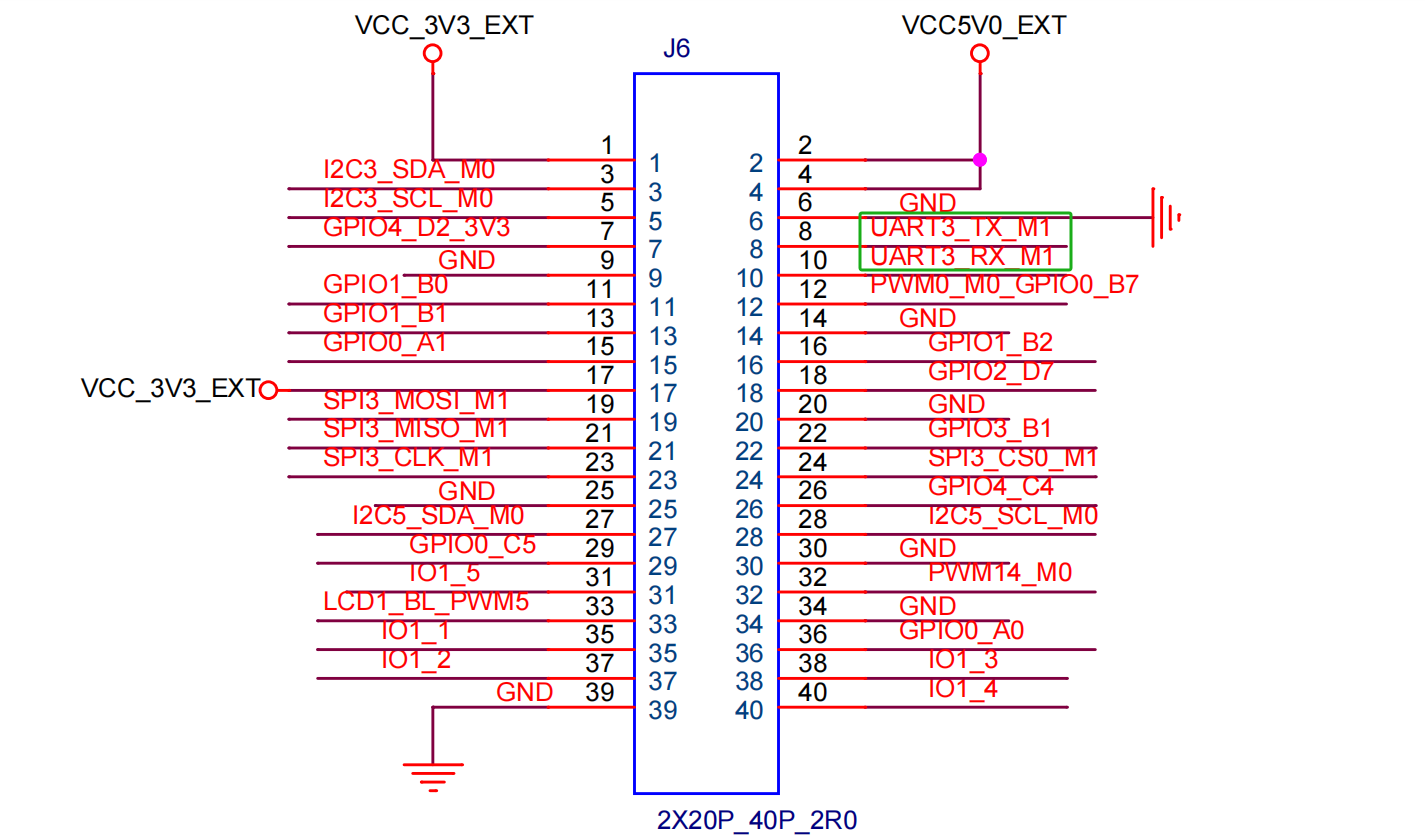
Correspondence of serial port pins (taking SC - 3568HA as an example)
| Serial port | PIN | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| TXD | 8 | Transmit signal line |
| RXD | 10 | Receive signal line |
Corresponding to UART3 on the 40 - PIN of the board
2. Check the serial port device
Check whether the serial port device is created
#Execute the command to view the serial port devices
ls /dev/ttyS*As shown in the figure, ttyS3 is UART3 and ttyS8 is UART8 (this serial port is occupied by the Bluetooth module)
3. Serial port communication test
Taking SC-3568HA as an example, conduct a serial port test by connecting a PC through a USB-to-serial port device
3.1 Connect to the serial port
Connect the TX and RX of the USB-to-serial port device to the UART3_RX and UART3_TX on the 40PIN respectively
The USB-to-TTL serial port device is shown in the following figure:
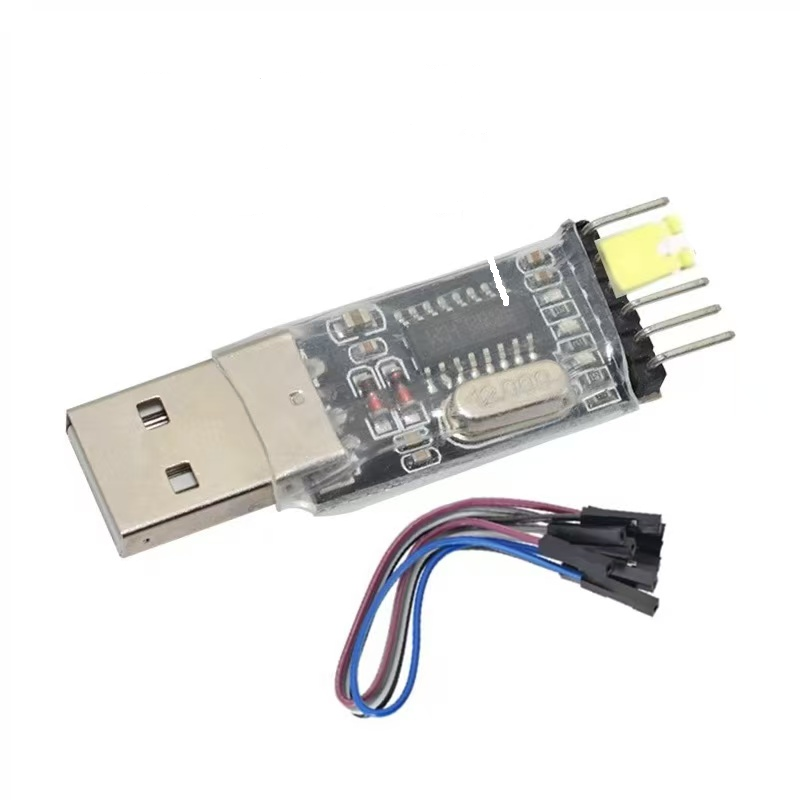

- TXD -- RXD
- RXD -- TXD
- GND -- GND
3.2 Query the serial port parameters and modify the baud rate
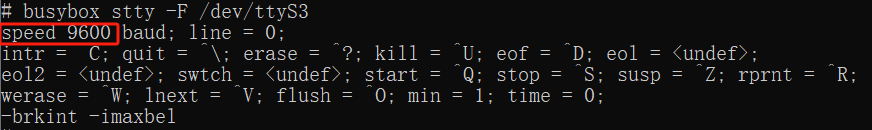
Use the stty tool to query the serial port parameters
#Execute the following commands in the terminal of the board
busybox stty -F /dev/ttyS3As shown in the figure:
Use the stty tool to modify the serial port parameters
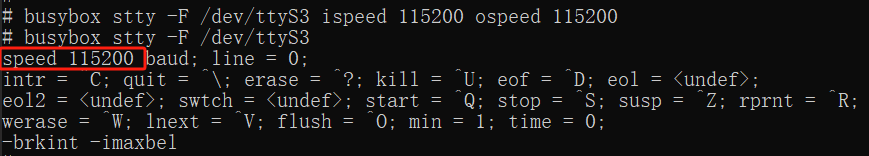
#Set the communication rate, where ispeed is the input rate and ospeed is the output rate
busybox stty -F /dev/ttyS3 ispeed 115200 ospeed 115200As shown in the figure:
Warning
The baud rate needs to be reset every time the device is powered on. By default, the baud rate will be reset to 9600 after a restart
3.3 Communicate with the PC
After configuring the serial port debugging assistant on the PC side, use the following command on the board side to test the serial port data sending:
Tips
Download address and path of the serial port tool:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ZUn2BNg-Sb6M-fWhDqAFMw?pwd=smcc 提取码:smcc
ShimetaPi开源鸿蒙资料>02-软件工具>Rockchip>OpenHarmony>串口工具>sscom5.13.1.exe
#Execute the following instructions in the terminal on the board
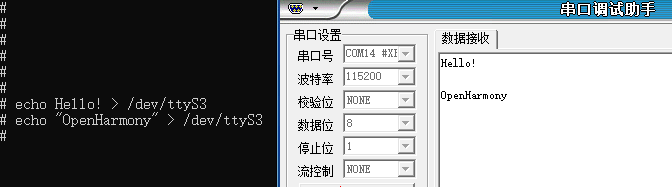
#Use the echo command to write the strings "Hello!" and "OpenHarmony!" to the terminal device file.
echo Hello! > /dev/ttyS3
echo "OpenHarmony" > /dev/ttyS3
#The serial port debugging assistant on the PC will receive the contentAs shown in the figure:
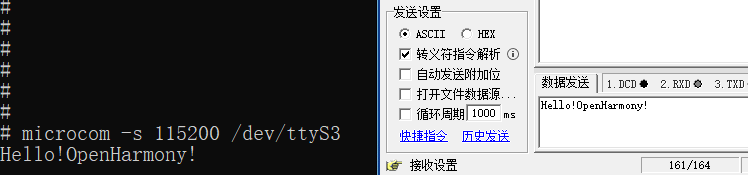
To test data reception, you can use the microcom tool:
#Execute the following instructions in the terminal of the board
#Use the microcom command to read the terminal device file. The -s parameter can be used to set the baud rate
microcom -s 115200 /dev/ttyS3
#The microcom command will wait
#Use the serial port debugging assistant to send a string
#The terminal of the board will output the received contentAs shown in the figure: