02 RS485
1 RS485 pin correspondence
White triangle corresponds to the first pin of the terminal - GND
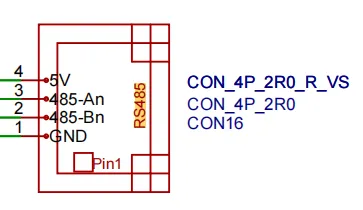

2 Check RS485 device
# 执行命令查看串口设备
ls /dev/ttyS*As shown in the figure, ttyS5 is the device node corresponding to RS485

3 RS485 communication test
3.1 Connecting RS485
Connect the USB to RS485 devices A to A, B to B.
● 5V -- 5V ● A -- A ● B -- B ● GND -- GND
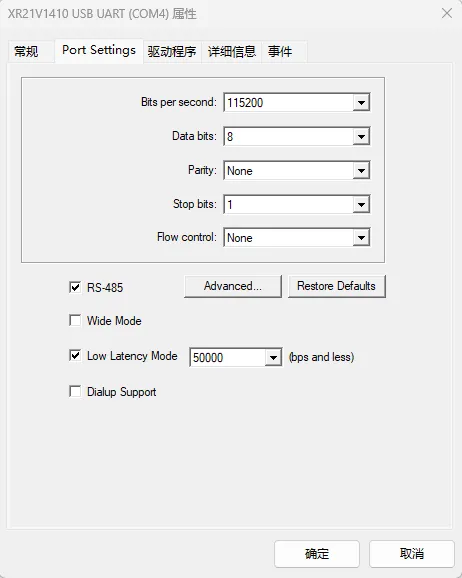
3.2 Set PC port configuration
Open the Device Manager → Port → Right-click the corresponding COM device and select Properties. Enter the device's properties interface, select Port Settings and check RS-485, as shown below
Notice
If the device corresponding to USB to RS485 is not found, please check whether the connection is correct and whether the driver is installed.
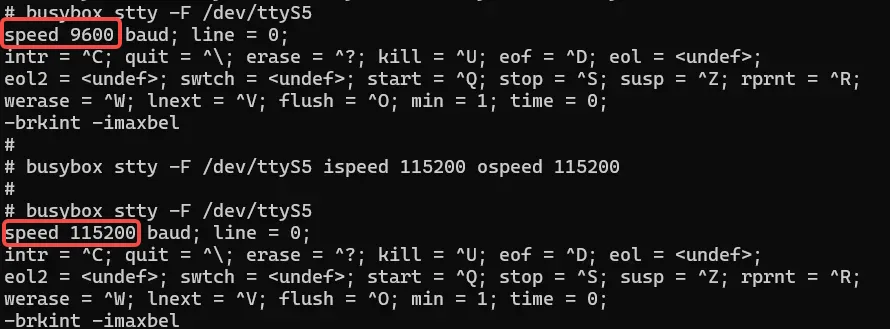
3.3 Query RS485 parameters and modify baud rate
# 在板卡的终端执行如下命令
busybox stty -F /dev/ttyS5
#设置通讯速率,其中ispeed为输入速率,ospeed为输出速率
busybox stty -F /dev/ttyS5 ispeed 115200 ospeed 115200As shown in the figure:
Notice
The baud rate needs to be reset every time the device is turned on. The default baud rate is reset to 9600.
3.4 Communication with PC
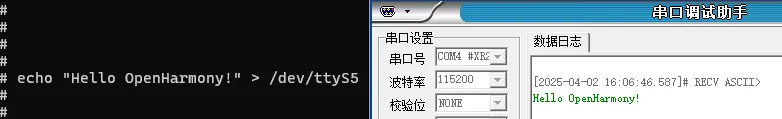
3.4.1 RS485 Send Data
After configuring the serial port debugging assistant on the PC, use the following command on the board to test the serial port sending data:
#在板卡上的终端执行如下指令
#使用echo命令向终端设备文件写入字符串"Hello OpenHarmony!"
echo "Hello OpenHarmony!" > /dev/ttyS5As shown in the figure, the serial port debugging assistant on the PC will receive the content
3.4.2 RS485 receiving data
#在板卡上的终端执行如下指令
#使用microcom命令读取终端设备文件,-s参数可以设置波特率
microcom -s 115200 /dev/ttyS5
#microcom命令会等待Use the serial port debugging assistant to send data, and the board's terminal will output the received data, as shown in the figure:

